Student loans are a crucial aspect of higher education financing, allowing students to pursue their academic dreams. However, understanding the intricacies of student loans is essential to make informed decisions. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the types of student loans, eligibility criteria, application processes, repayment options, and much more.
Types of Student Loans
Student loans fall into two primary categories: federal student loans and private student loans.
Federal Student Loans
Federal student loans are offered by the U.S. Department of Education and come with numerous advantages:
- Lower interest rates
- Flexible repayment options
- Loan forgiveness programs
- Deferment and forbearance options
- No credit check (for most federal loans)
Private Student Loans
Private student loans are provided by banks, credit unions, and online lenders. While they can fill in the gaps when federal loans fall short, they often have higher interest rates and may require a credit check or a co-signer.
Eligibility Criteria
To qualify for federal student loans, you must meet specific eligibility criteria, including:
- U.S. citizenship or eligible non-citizenship status
- A valid Social Security number
- Enrollment in an eligible degree or certificate program
- Satisfactory academic progress
- Compliance with Selective Service registration requirements
Applying for Federal Student Loans
FAFSA Application
The first step in applying for federal student loans is completing the Free Application for Federal Student Aid (FAFSA). This application determines your eligibility for federal grants, work-study, and loans.
Understanding Your EFC
After submitting the FAFSA, you will receive a Student Aid Report (SAR) that includes your Expected Family Contribution (EFC). Your EFC helps determine your eligibility for need-based financial aid.
Federal Student Loan Programs
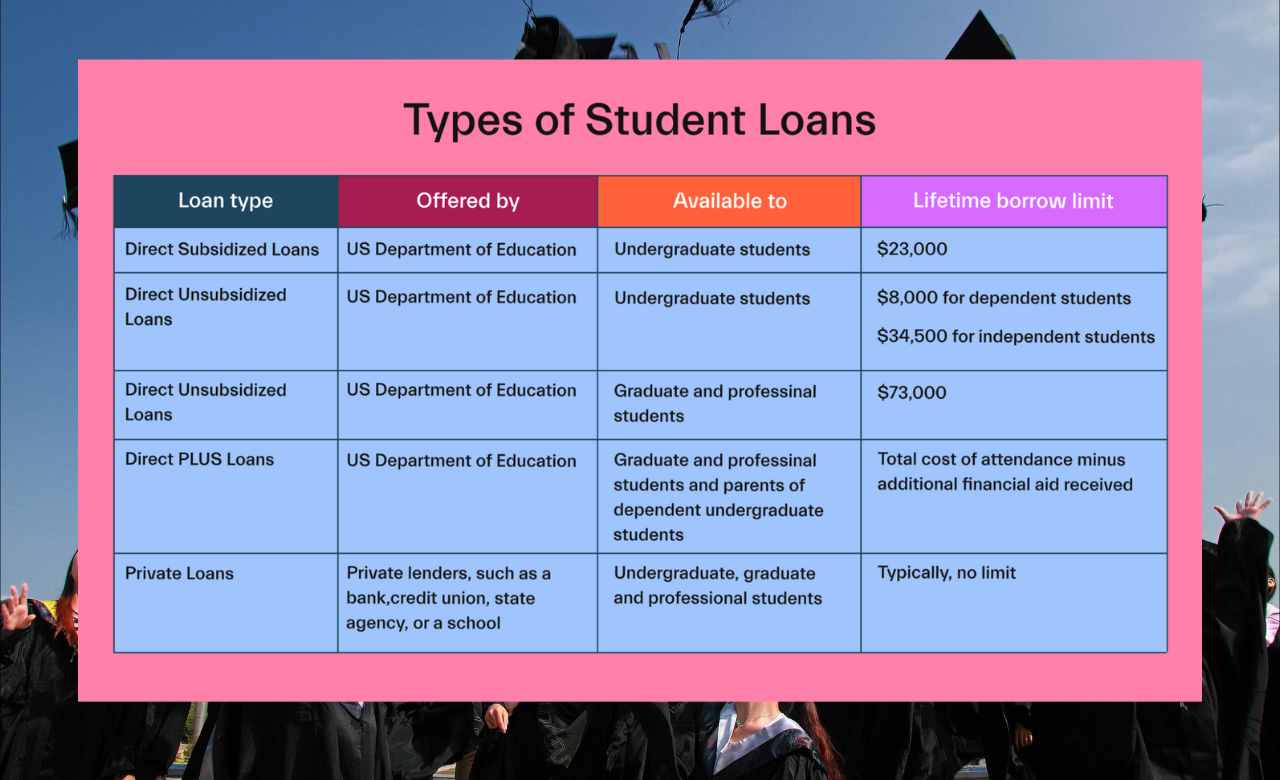
Direct Subsidized Loans
Direct Subsidized Loans are available to undergraduate students with financial need. The government pays the interest while you are in school, during the grace period, and during deferment.
Direct Unsubsidized Loans
Direct Unsubsidized Loans are available to undergraduate and graduate students regardless of financial need. Interest accrues from the time the loan is disbursed.
PLUS Loans
PLUS Loans are available to parents of dependent undergraduate students and graduate students. They require a credit check and may cover the cost of attendance.
Repayment Plans
Repaying your student loans is a crucial aspect of the process. The federal government offers various repayment plans to accommodate different financial situations.
Standard Repayment Plan
The Standard Repayment Plan has fixed monthly payments over ten years. It is the fastest way to pay off your loans but may have higher monthly payments.
Income-Driven Repayment Plans
Income-Driven Repayment Plans adjust your monthly payments based on your income and family size. These plans include Income-Based Repayment (IBR), Pay As You Earn (PAYE), and Revised Pay As You Earn (REPAYE).
Private Student Loans: What You Need to Know
While federal student loans are often the first choice due to their favorable terms, private student loans can fill gaps in financing. However, it’s essential to understand that private loans typically have higher interest rates and less flexible repayment options.
Pros and Cons of Student Loans
Before taking out student loans, consider the advantages and disadvantages.
Pros:
- Access to education
- Potential for higher income with a degree
- Opportunity to build credit
Cons:
- Accumulation of debt
- Interest accrual
- Monthly payments after graduation
Tips for Managing Student Loan Debt
Managing student loan debt requires a thoughtful approach. Here are some tips:
- Create a budget
- Explore loan forgiveness programs
- Make on-time payments
- Consider loan consolidation
Loan Forgiveness and Cancellation Programs

Loan forgiveness and cancellation programs can help alleviate the burden of student loan debt. These programs are often available for public service, teaching, and income-driven repayment plans.
Avoiding Student Loan Scams
Beware of scams targeting student loan borrowers. Verify the legitimacy of any company or service offering student loan assistance.
Conclusion
Student loans can open the doors to higher education and career opportunities. However, they come with responsibilities. Understanding the various aspects of student loans is crucial for making informed decisions about your education financing.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are student loans the only option for financing education?
No, there are other options such as scholarships, grants, work-study programs, and personal savings. It’s advisable to explore all sources of funding before considering student loans.
Can I defer my student loans while in school?
Yes, federal student loans typically offer deferment options while you are enrolled in school at least half-time. Interest may still accrue on unsubsidized loans.
How does interest accrue on student loans?
Interest accrues on most student loans, including federal unsubsidized loans, from the time they are disbursed. The interest rate and accrual details vary by loan type.
What is loan consolidation, and should I consider it?
Loan consolidation combines multiple federal loans into one, simplifying repayment. It can be helpful for managing loans, but it may extend the repayment term and result in higher interest costs.
How can I lower my monthly student loan payments?
You can lower monthly payments by enrolling in an income-driven repayment plan, which adjusts your payments based on your income and family size.

